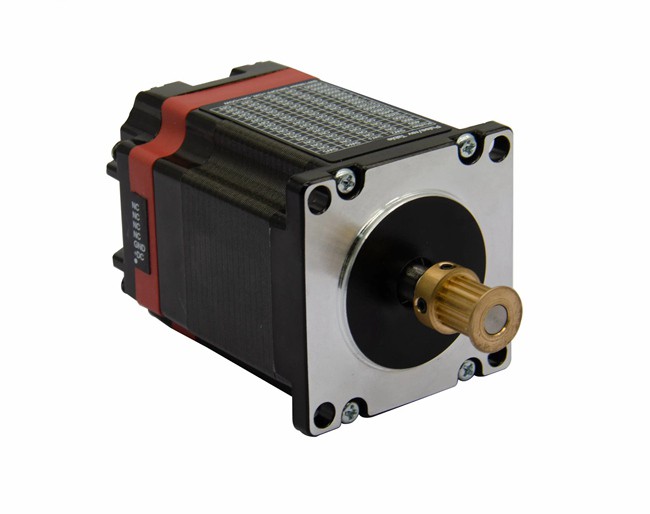
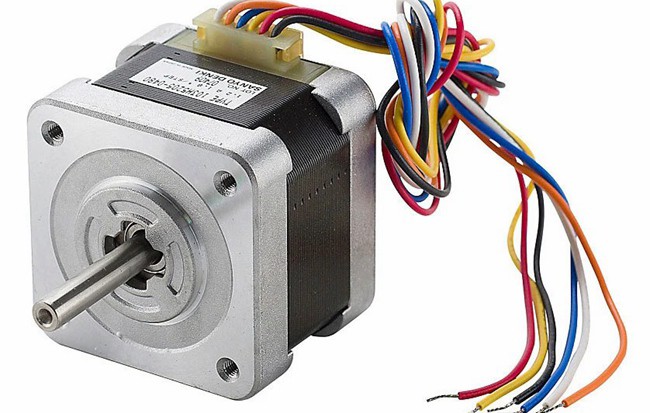
High Torque tepper Motor NEMA 23/Stepping Motor/Step Motor with ISO and CE
Product description
The working principle of a reactive stepper motor is relatively simple, with many small teeth evenly distributed on the rotor. The stator teeth have three excitation winding resistances, and their geometric axes are sequentially offset from the rotor tooth axis. The position and speed of the motor correspond one-to-one with the number of conductive pulses and frequency. The direction is determined by the order of conductivity. Generally, reactive stepper machines with two, three, four, and five phases are predominant in the market.

Stepper motor, also known as pulse motor, works based on electromagnetic principles and generates electromagnetic torque through changes in air gap magnetic conductivity. Every time a pulse signal is input, the rotor of the stepper motor will rotate at a fixed angle or move forward one step. The output angular displacement or linear displacement is proportional to the number of input pulses, and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency. This characteristic makes stepper motors very suitable for application scenarios that require precise control of position and speed.


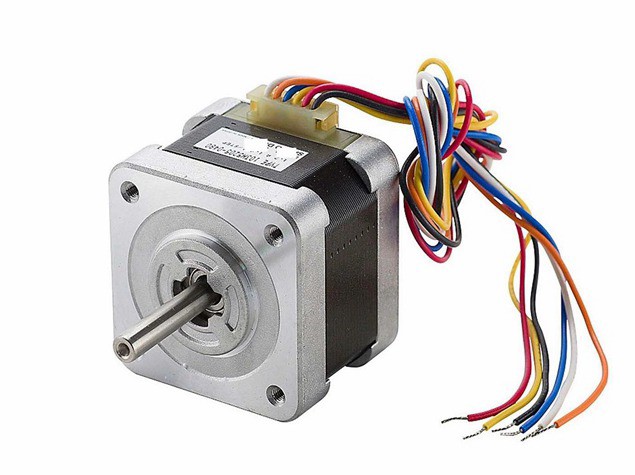

Recommended products