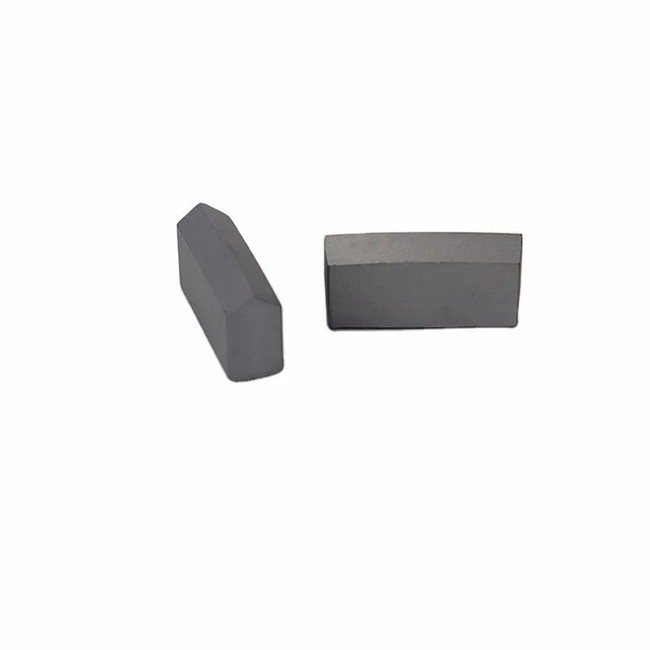
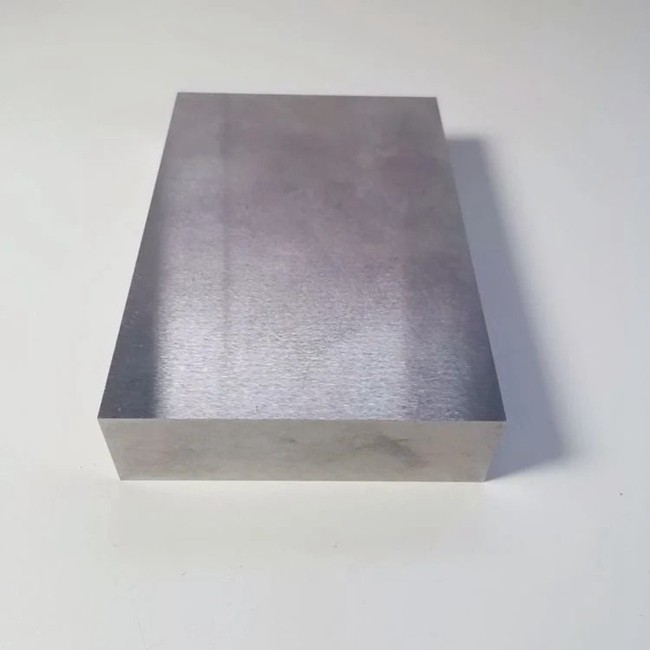
Professional Wear Block Cemented Tungsten Carbide Tool Parts
Product description
Tungsten carbide is used in the manufacture of a variety of wear-resistant parts and components such as bearings, sealing rings, and nozzles. These parts maintain long service life and stable performance when operating at high speeds, high temperatures, high pressures or in corrosive environments. Tungsten carbide coatings and films are widely used in mechanical parts, electronic components, medical devices and other fields due to their excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance and high temperature stability. These coatings and films can be prepared by chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition and other methods to improve the surface properties of the base material.
In the aerospace field, tungsten carbide is used to manufacture high-temperature components such as nozzles for jet engines and blades for gas turbines. These components are required to operate at high temperatures, high speeds and in harsh environments, and tungsten carbide's high melting point and excellent thermal stability make it an ideal choice. Tungsten carbide is also used in the manufacture of ceramic cutting tools, abrasives and grinding tools. In ceramic processing, glass processing, stone processing and other industries, tungsten carbide tools are favored for their high hardness and wear resistance.
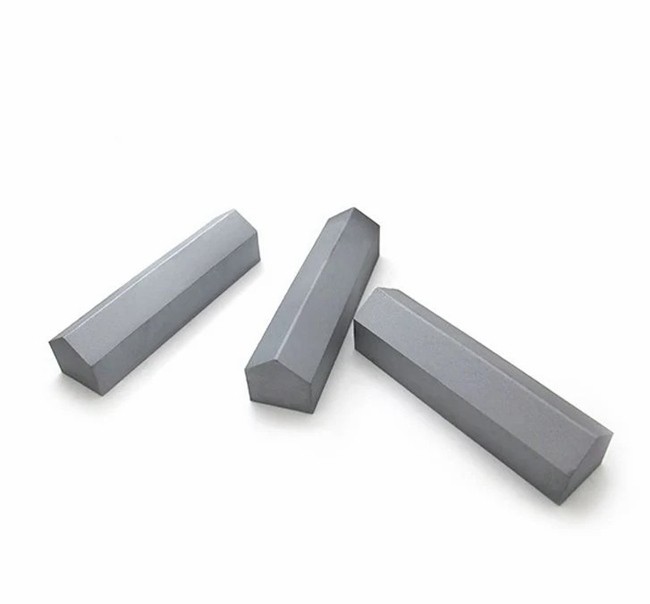

Tungsten carbide, a black hexagonal crystal synthesized from the elements tungsten and carbon through a specific process at high temperature, has a metallic luster. Its extreme hardness, second only to diamond in nature, makes it one of the hardest known metal carbides. This extraordinarily high hardness gives tungsten carbide excellent wear and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for many industrial applications.

Tungsten carbide is usually prepared by carbothermal reduction, powder metallurgy or chemical vapor deposition. Among them, powder metallurgy is one of the most commonly used methods, which is made by mixing tungsten and carbon powders, pressing them into shape, and then sintering them at high temperatures. This method is not only a mature process, but also capable of producing tungsten carbide products with complex shapes and excellent performance.


Recommended products




