Your Guide to Bicycle Brakes: Safety, Performance, and Choosing the Right System
Product description
A bicycle's brakes are its most critical safety component. More than just a way to stop, a high-quality braking system provides the confidence to enjoy your ride, whether you're navigating city streets, descending a mountain trail, or simply cruising with the family. Understanding how brakes work, the different types available, and how to maintain them is essential for every cyclist. This guide will help you make an informed decision to ensure your bike stops as reliably as it goes.
Understanding Bicycle Brake Systems: Types and Core Features
The two most common modern brake systems are disc brakes and rim brakes, each with distinct characteristics.
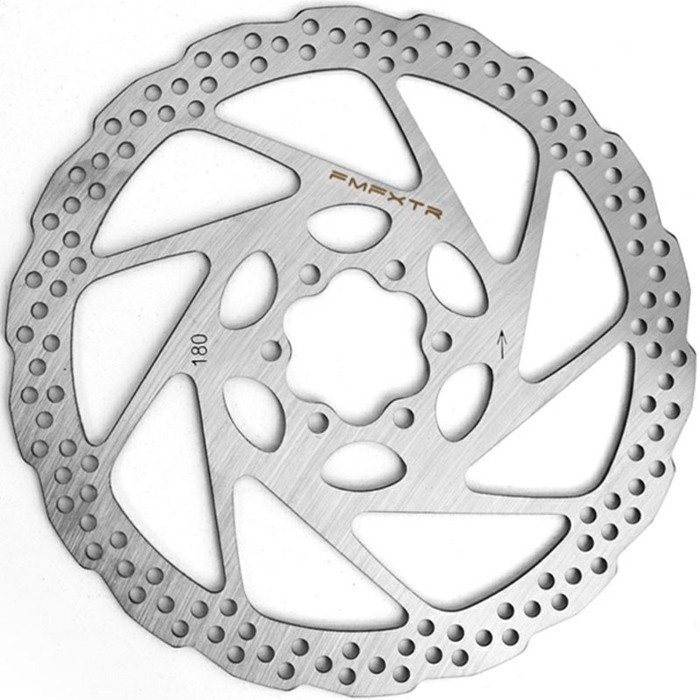

Disc Brakes:
- Power and Consistency: Disc brakes use a rotor attached to the wheel hub and a caliper that squeezes brake pads against it. This design provides exceptional stopping power and performs consistently in all weather conditions, including rain and mud.
- Types: Hydraulic disc brakes offer self-adjusting pads, modulated control, and are generally considered top-tier for performance. Mechanical (cable-actuated) disc brakes are easier to maintain and offer a significant performance upgrade over rim brakes.
- Heat Dissipation: The rotor is separate from the rim, allowing for better heat dissipation on long descents, which prevents brake fade.
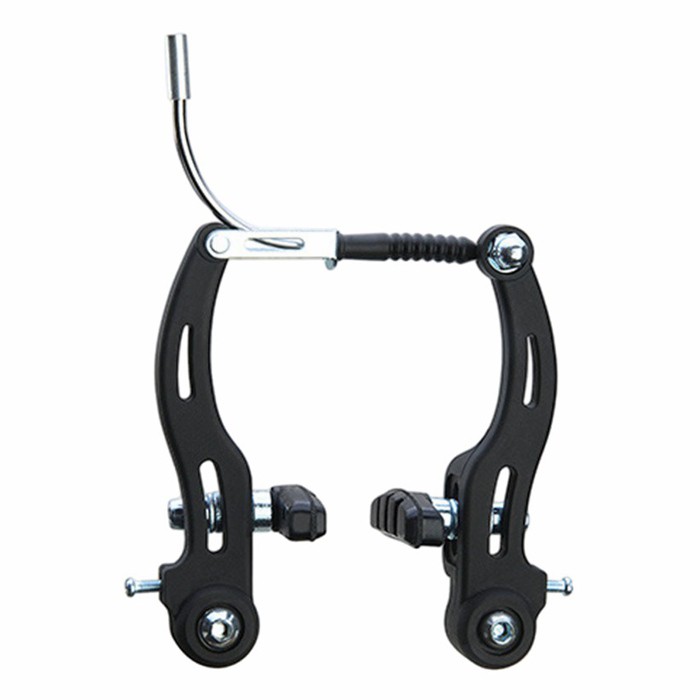

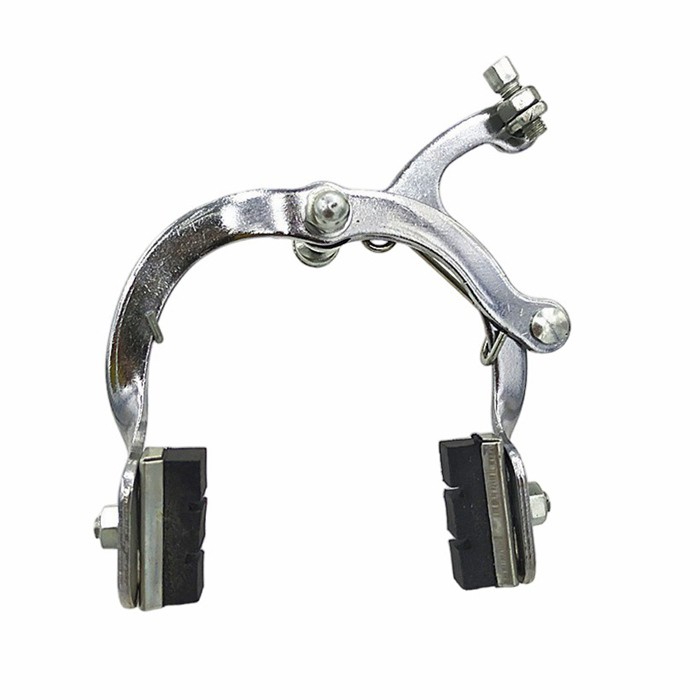
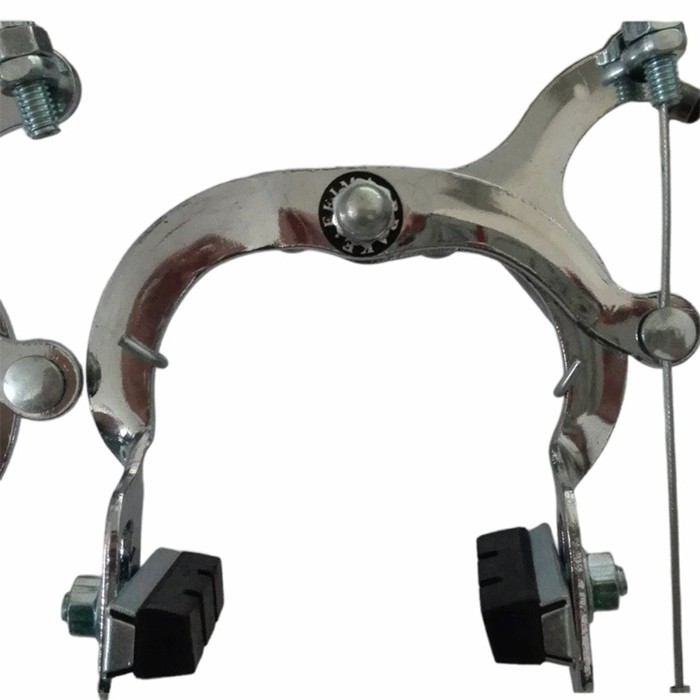
Rim Brakes:
- Lightweight and Simple: These brakes, including caliper, cantilever, and V-brakes, function by squeezing brake pads against the wheel's rim.
- Ease of Maintenance: They are lightweight, generally less expensive, and straightforward to adjust and repair.
- Weather Limitations: Their performance can significantly decrease in wet or dirty conditions as the pads grip a wet or grimy surface.
Key Advantages of a Well-Maintained Braking System
Investing in the right brakes and maintaining them properly delivers undeniable benefits.
- Enhanced Safety and Control: Reliable brakes are the foundation of safe cycling, allowing for controlled slowing and confident stopping in unexpected situations.
- All-Weather Reliability: Especially with disc brakes, you can trust your ability to stop whether the roads are wet, dry, or covered in trail debris.
- Improved Riding Confidence: Knowing you can stop effectively allows you to ride more assertively, enjoy higher speeds on descents, and handle technical terrain with greater assurance.
- Modulation: High-quality brakes allow for precise control over braking force, enabling you to slow down gradually without locking up the wheels.
Primary Applications and Bike-Specific Considerations
The ideal brake system often depends on the type of cycling you do.
- Mountain Biking: Hydraulic disc brakes are the undisputed standard, essential for handling steep, technical descents and variable trail conditions.
- Road Biking: Disc brakes (both hydraulic and mechanical) have become the norm for new models, offering better performance in all conditions. Some lightweight road bikes still use high-quality caliper rim brakes.
- Commuting and Hybrid Bikes: Disc brakes are highly recommended for consistent all-weather performance in stop-and-go traffic. V-brakes are a common and cost-effective alternative on many hybrid models.
- Recreational and Kids' Bikes: Coaster (back-pedal) brakes or simple rim brakes are often sufficient for casual, fair-weather riding on flat terrain.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bicycle Brakes
1. Are disc brakes really worth the extra cost over rim brakes?
For most riders, yes. The superior stopping power and all-weather consistency of disc brakes provide a significant safety margin. If you regularly ride in hills, in the rain, or on trails, disc brakes are a worthwhile investment.
2. How often should I replace my brake pads?
There's no fixed timeline; it depends on riding conditions and habits. Inspect them regularly. For rim brakes, replace pads when the grooves on the surface are nearly gone. For disc brakes, replace them when the pad material wears down to less than 3mm thick. Squealing or reduced braking power are also key indicators.
3. My brakes are making a squealing noise. What's wrong?
Squealing is often caused by contamination (e.g., oil on the rotor or rim), misaligned brake pads, or glazed pads. For disc brakes, try cleaning the rotor with isopropyl alcohol. For both disc and rim brakes, inspect the pads for wear or contamination and ensure they are properly aligned with the braking surface.
4. Can I upgrade my bike from rim brakes to disc brakes?
This is often complex and usually not cost-effective. It requires a frame and forks with disc brake mounts, new wheels with rotor hubs, and the entire new brake system. It is generally more practical to purchase a new bike designed for disc brakes.
5. What is "brake rub" and how can I fix it?
Brake rub occurs when a disc brake pad lightly contacts the rotor even when the brake is not applied, creating a scraping sound. It's a common issue often fixed by simply loosening the caliper mounting bolts, squeezing the brake lever firmly, and re-tightening the bolts to re-center the caliper.
Stop with Confidence
Your bicycle's brakes are not a component to compromise on. Understanding the differences between systems and committing to regular maintenance ensures every ride is a safe and enjoyable experience. Whether you're upgrading your current bike or selecting a new one, prioritizing a high-quality braking system is an investment in your safety and cycling pleasure.
Explore our comprehensive range of brake systems, replacement pads, and maintenance tools to find the perfect setup for your riding style.
Recommended products